
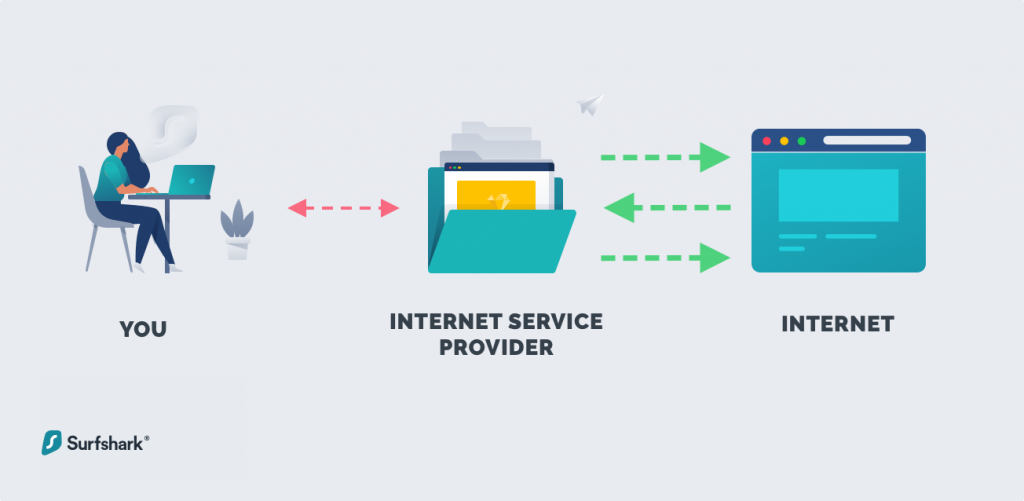
Their network is connected to the WAN which is better known as the internet. Internet Service Providers run a Wide Area Network (WAN) in their service areas. (Think the 5 freeway in Los Angeles at rush hour.) The more traffic on the network, the slower things run. On the internet, the servers are best defined as the machines that serve up the websites and other online content – such as video and audio – that you access from your computer or mobile devices, which are the “client” part of the equation.Įvery network – even one as large as the internet – only has a limited amount of bandwidth available. Clients are computers and other devices on the network that request data from the servers. Servers are specially set up computers that store massive amounts of data, which are accessed by clients. Throttling is usually a reactive measure used by ISPs and other types of communication networks to regulate a network’s traffic and alleviate network congestion.Īny network is made up of servers and clients. Throttling is best defined as when your Internet Service Provider (ISP) intentionally slows the speed of your broadband internet connection. Welcome to the wonderful world of ISP throttling. You pay for a 60 Mbps connection – and yet, you see speed numbers like this:

Spectrum throttling internet 1080p#
Is that pixelization? And why does Netflix indicate you’re watching their 1080p stream?
Suddenly, you notice the video isn’t quite as sharp as it had been. You’re in the 10th straight hour of a weekend Cobra Kai binge on Netflix, enjoying all of the 4K HDR goodness that is Johnny Lawrence on your new UHD Smart TV.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
